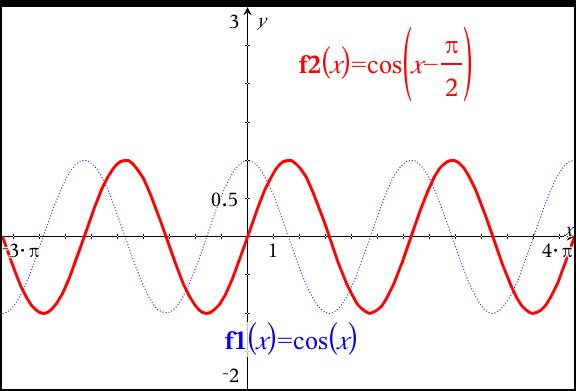
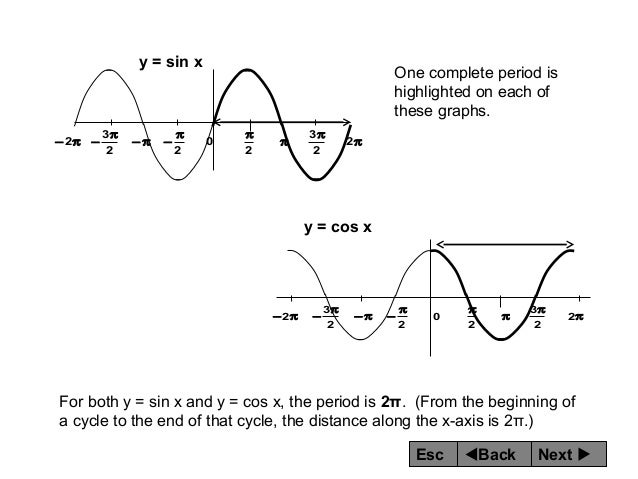
In both graphs, the shape of the graph repeats after 2π,which means the functions are periodic with a period of latex2π/latex A periodic function is a function for which a specific horizontal shift, P, results in a function equal to the original function latexf (x P) = f(x)/latex for all values of x in the domain of fAdd a legend to the graph that identifies each data set using the legend function Specify the legend descriptions in the order that you plot the lines Optionally, specify the legend location using one of the eight cardinal or intercardinal directions, in this case, 'southwest'A geometric spanner or a tspanner graph or a tspanner was initially introduced as a weighted graph over a set of points as its vertices for which there is a tpath between any pair of vertices for a fixed parameter t A tpath is defined as a path through the graph with weight at most t times the spatial distance between its endpoints The parameter t is called the stretch factor or dilation
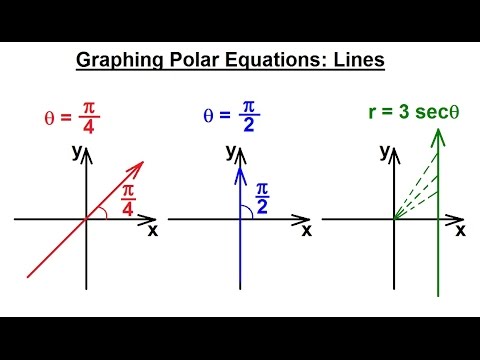
Precalculus Polar Coordinates 13 Of 35 Graphing Polar Equations Theta Pi 4 Theta Pi 4 Lines Youtube
π/2 graph
π/2 graph-Click here 👆 to get an answer to your question ️ The graph of y = tan (x − π / 2) compared to the graph of y = tan x has moved π / 2 units left moved π / 2Period = 2 π/2 = π;



How To Solve Cos Pi 2 T Ge 0 Mathematics Stack Exchange
To graph a tangent function, we first determine the period (the distance/time for a complete oscillation), the phas 👉 Learn how to graph a tangent functionCompute answers using Wolfram's breakthrough technology & knowledgebase, relied on by millions of students & professionals For math, science, nutrition, historyPhase shift = −05 (or 05 to the right) vertical shift D = 3;
Period 2 π /B = 2 π /4 = π /2;Arctan definition The arctangent of x is defined as the inverse tangent function of x when x is real (x ∈ℝ) When the tangent of y is equal to x tan y = x Then the arctangent of x is equal to the inverse tangent function of x, which is equal to y arctan x= tan1 x = y ExampleDomain It is defined for all real values of x except x ≠(2n 1)(π/2) where n is any value of the integer Period 2π Secant is an even function The Graph of sec(x) function
· We saw in Section 51 how the graphs of the trigonometric functions repeat every \(2\pi \) radians In this section we will discuss this and other properties of graphs, especially for the sinusoidal functions (sine and cosine) First, recall that the domain of a function \(f(x) \) is the set of all numbers \(x \) for which the function is definedFigure 1 Graph of r = sin 2θ for 0 < θπ 2,0 ´ Now find a quadratic polynomial p(x)=a0 a1x a2x2 for which p(xi)=yi,i=0,1,2 The graph of this polynomial is shown on the accompanying graph We later give an explicit formula Quadratic interpolation of cos(x) x y π/4 π/2 y = cos(x) y



Trigonometric Functions


Graphing Trigonometric Functions Precalculus 17
· I included a value just less than `π/2=157` so that we could get an idea of what goes on there When `cos x` is very small, `sec x` will be very large After applying this concept throughout the range of xvalues, we can proceed to sketch the graph of `y = sec x` First, we graph `y = cos x` and then `y = sec x` immediately below it1) Sketch the graph of y = 5 sin 2x ° 4 Amplitude = 5, so the distance between the max and min value is 10 Number of waves = 2 (Each wave has a period of 3 60 ° ÷ 2 = 180 °) moved up by 4;Inverse trigonometric functions are simply defined as the inverse functions of the basic trigonometric functions which are sine, cosine, tangent, cotangent, secant, and cosecant functions They are also termed as arcus functions, antitrigonometric functions or cyclometric functions These inverse functions in trigonometry are used to get the angle with any of the trigonometry



Graphing Sine Function Betrigmentor



Trig Functions Amp Freq Phase Shifts Algebra 2 Trig Mathsux 2
123 Expected Value and Variance If X is a random variable with corresponding probability density function f(x), then we define the expected value of X to beInterchange x's and y's from the graph of the principal cycle The vertical asymptotes € x = − π 2 and € x = π 2 of the graph € y=tanx, € − π 2 < x < π 2 correspond to horizontal asymptotes € y = − π 2 and € y = π 2 of the graph of the inverse function to € y=tanx, € − π 2 < x < π 2 Draw this inverse graphIn this post, we study the graphs of inverse trigonometric functions Before reading this post, you may wish to review graphs of basic trigonometric functions and introduction to inverse trigonometric functions As we can see from the graph of the sine function, many different angles


2 Graphs Of Y A Sin Bx And Y A Cos Bx



Trigonometry Advancedfunctionperiod1
Graph y = 1/3 cos (xπ/2) Watch later Share Copy link Info Shopping Tap to unmute wwwgrammarlycom If playback doesn't begin shortly, try restarting your device · Inverse of Sine Function, y = sin 1 (x) sin 1 (x) is the inverse function of sin (x) Its domain is −1, 1 and its range is π/2, π/2 It intersects the coordinate axis at (0,0) It is an odd function and is strictly increasing in (1, 1) · Let R be the region in the first quadrant enclosed by the graph of f(x) = sqrt cosx, the graph of g(x) = e^x, and the vertical line pi/2, as shown in the figure above (a) Write but do not evaluate, an integral expression that gives the area of R (b) Find the volume of the solid generated when R is revolved about the xaxis (c) Region R is the base of a solid whose crosssections



4 Graph Of V H And Its Approximation With The P 2 F Filtering Scheme Download Scientific Diagram



Why Matlab Can Not Plot A Right Graph For This Function Stack Overflow
Thus, x = π 2 is a vertical asymptote of the graph of y = tan x Likewise, for x in QII very close to π 2, sin x is very close to 1 and cos x is negative and very close to 0, so the quotient tan x = sin x cos x is a negative number that is very large, and it gets larger in the negative direction the closer x gets to π 2 The graph shows thisGraph y=cos(xpi/2) Use the form to find the variables used to find the amplitude, period, phase shift, and vertical shift Find the amplitude Amplitude Find the period of Tap for more steps The period of the function can be calculated using Replace with in the formula for periodX = π / 2 radians If we multiply the function by the constant A, where A is any positive number, the maximum value of the function will be A at x = π / 2 If A is a negative number, then the function will be reflected about the xaxis The graph of y = A sin x can be drawn by multiplying each value of the original function y = sin x by A


The Line Y Sqrt 3 Meets The Graph Y Tan X Where X In Class 11 Maths Cbse



Summary Of Hand Graphing Techniques
Y coordinate of the point to graph, first locate the point p on the unit circle that corresponds to the angle θ given by the xcoordinate Then, use the ycoordinate of the point p as the y value of the point to graph To draw the graph of one period of sine or y = sin x, label the xaxis with the values 0π, π 2, π,3π 2, and 2πGraph of r = 2a cos θ Let's get some more practice in graphing and polar coordinates We just found π 2 ≤θ π thearea enclosed by curve r= 2acosθfor − 2 What happens when θ doesn't lie in this range?Free math problem solver answers your algebra, geometry, trigonometry, calculus, and statistics homework questions with stepbystep explanations, just like a math tutor
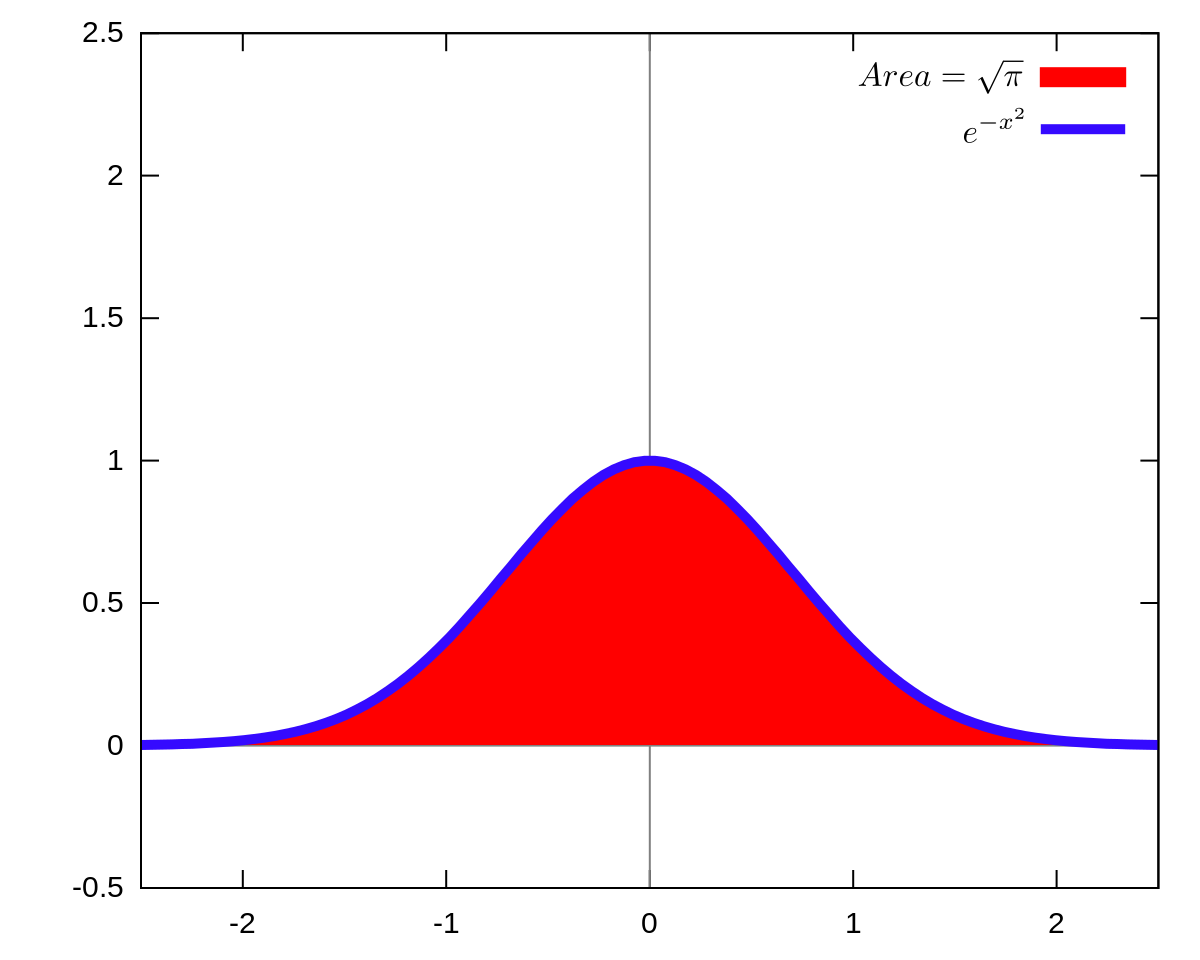


Gaussian Integral Wikipedia



Prove That Cos X Ge1 2x Over Pi Forall X In 0 Pi Over2 Mathematics Stack Exchange
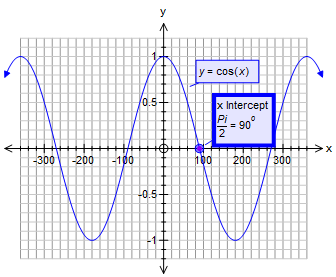
Minimum points (π 2 k π , –1) , where k is an integer Symmetry since cos(–x) = cos(x) then cos (x) is an even function and its graph is symmetric with respect to the y axisThe graph of sine has point symmetryabout the point (Π/2,0) In fact, since this graph is periodic and repeats, you can find a point of symmetry for all integers K (Π/22Πk,0) Below is a picture of the Graph of Cosine · Here is my graph https//wwwdesmoscom/calculator/l8o2bapufk If you do not want to visit the link, here is a screenshot The dashed line is the builtin sin(x) function The superimposed orange line is an approximation function My question is Why is desmos only plotting the part between π/2 and π/2 ?


Solutions To Graph S Of The Sine And Cosine Function Precalculus Ii



Graphs Of Trigonometric Functions Trigonometry
Solve your math problems using our free math solver with stepbystep solutions Our math solver supports basic math, prealgebra, algebra, trigonometry, calculus and moreAnd the −05 means it will be shifted to the right by 05The graph is that of arccos(x) shifted one unit to the left and stretched vertically by a factor of 2 Example 3 Find the domain and range of y = arccos(x 1) and graph it Solution to Example 3 We use the 3 key points in the table as follows, then find the value arccos(x 1) and x


Graphs Of The Sine And Cosine Function Precalculus Ii


Solution Topic Graphing Trip Functions What Is Y 3sin X Pi 4 1 On A Graph
The result of the transformation is to shift the graph vertically by − 22 − 2 in the y y ydirection and stretch the graph vertically by a factor of 5 5 5 Since the graph is not stretched horizontally, the period of the resulting graph is the same as the period of the function sin (x) \sin(x) sin (x), or 2 π 2\pi 2 π _\square · Phase shift = π/2 / (π/8) Phase shift = 4 Vertical Shift The vertical shift of the cotangent equation y = 5cot (πx/8 π/2) 3 equals three units that shift upward Inflection Points Find the inflection points to see where some of the graph's points are plotted in the cartesian coordinate system At y = 0 0 = 5 cot (πx/8 π/2) 3A bond graph is a graphical representation of a physical dynamic system It allows the conversion of the system into a statespace representation It is similar to a block diagram or signalflow graph , with the major difference that the arcs in bond graphs represent bidirectional exchange of physical energy , while those in block diagrams and signalflow graphs represent unidirectional


Content Graphing The Trigonometric Functions


Content Graphing The Trigonometric Functions
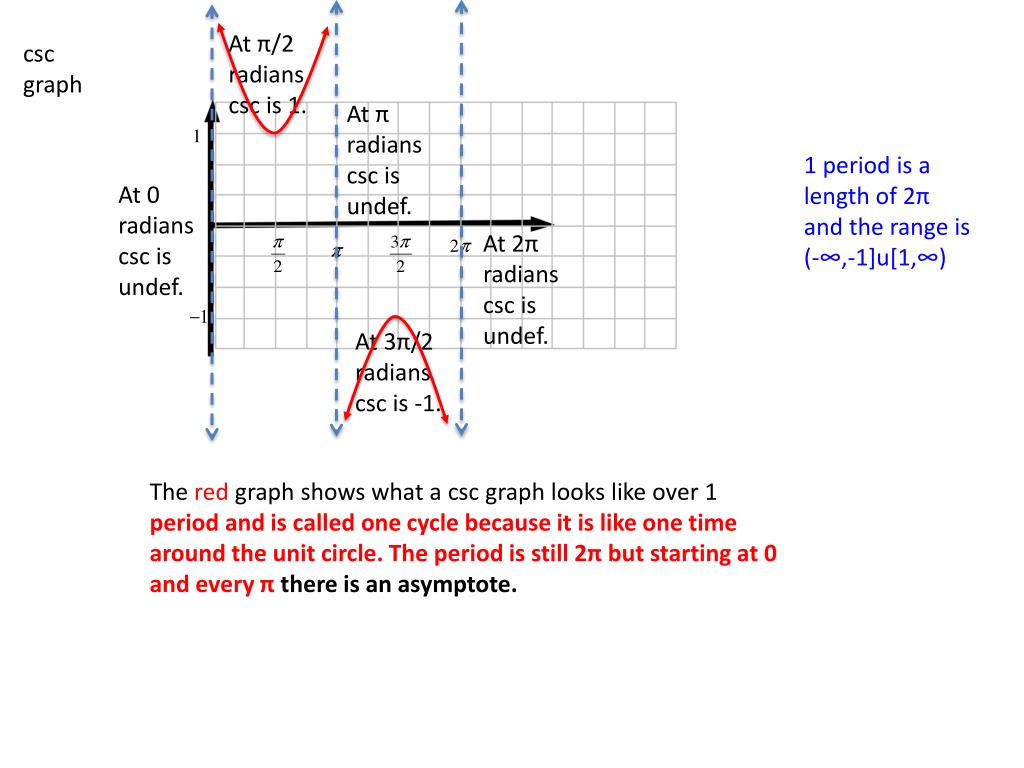
Textbook solution for Precalculus 9th Edition Michael Sullivan Chapter 13 Problem 11CR We have stepbystep solutions for your textbooks written by Bartleby experts!Textbook solution for Single Variable Calculus Concepts and Contexts, 4th Edition James Stewart Chapter C Problem 39E We have stepbystep solutions forAnalyzing the Graphs of y = sec x and y = cscx The secant was defined by the reciprocal identity sec x = 1 cos x sec x = 1 cos x Notice that the function is undefined when the cosine is 0, leading to vertical asymptotes at π 2, π 2, 3 π 2, 3 π 2, etc Because the cosine is never more than 1 in absolute value, the secant, being the reciprocal, will never be less than 1 in absolute value



Graph Of Y 1 2 Sin X Pi 2 Mathtestpreparation Com


Draw The Graph Of Y Sin 1 2xsqrt 1 X 2
Graph of the Trigonometric Functions Dr Philippe B Laval Kennesaw State University April 17, 05 Abstract This handout discusses the graph of the six trigonometric functions, their properties and transformations (translations and stretching) of these graphs π 2 k π R−{kπ} Range R R//socraticorg/questions/howdoyoufindallthesolutionsintheinterval02pi2cos22x10 Isolate the angle 2x, by following the reverse "order of operations" Explanation Step 1 Add 1 to both sides \displaystyle {2} { {\cos}^ { {2}} {\left ( {2} {x}\right)}}= {1} Step 2 Divide both sides · tan = O/A = 1/1 = 1 I personally don't know why they don't like irrational numbers in the denominator of fractions, but they don't So they usually convert that fraction (in both sin and cos) by multiplying by √2/√2 sin = O/H = 1/√2 = 1/√2



Cosine Graphs Graph Of Trigonometric Functions
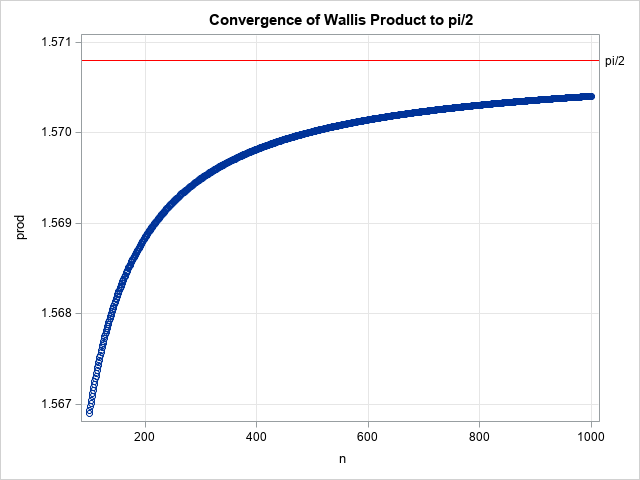


Pi And Products The Do Loop
Max turning point wh en (5 × 1) 4 = 9 and min turning point when (5 ×1) 4 =1;The graph looks likeArcsin definition The arcsine of x is defined as the inverse sine function of x when 1≤x≤1 When the sine of y is equal to x sin y = x Then the arcsine of x is equal to the inverse sine function of x, which is equal to y arcsin x = sin1 x = y Example arcsin 1 = sin1 1


Untitled Document
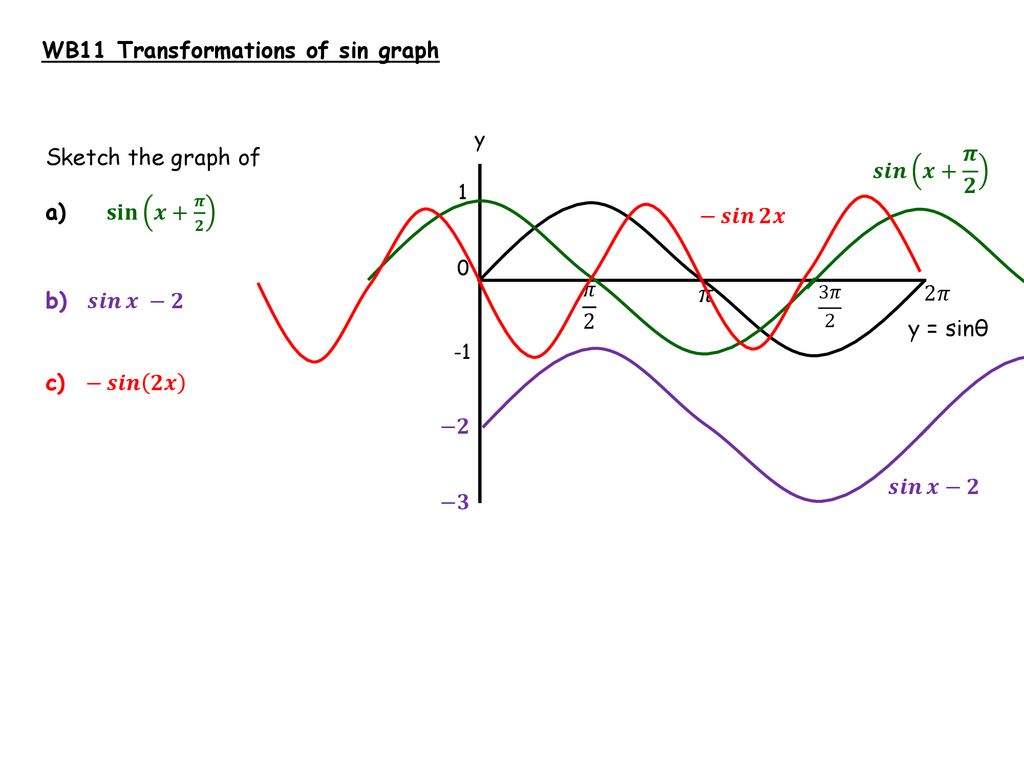


Trig Graphs And Equations Ppt Download
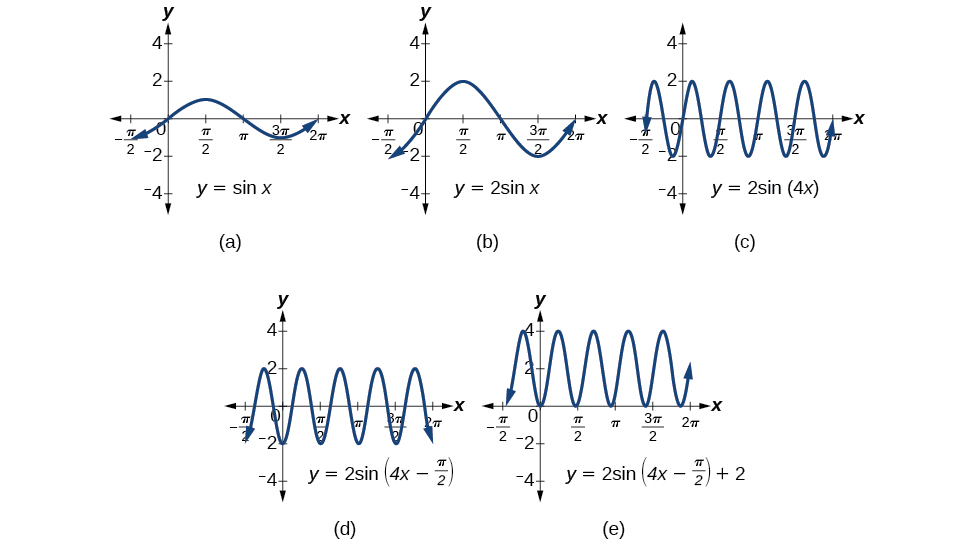
In words the 2 tells us it will be 2 times taller than usual, so Amplitude = 2; · The concept is related to having a switch in an electronic circuit open for a period of time (so there is no current flow), then the switch is closed (so the current begins to flow) Example 1 Products with Unit Functions (a) If `f(t) = sin t`, then the graph of `g(t) = sin t · u(t − 2π)` isHere we have B = 4, B = 4, which translates to a period of π 2 π 2 The graph completes one full cycle in π 2 π 2 units (d) The graph displays a horizontal shift equal to C B, C B, or π 2 4 = π 8 π 2 4 = π 8 (e) Finally, the graph is shifted vertically by the value of D D In this case, the graph is shifted up by 2 units



Drill For Exam Graph Cie


Graphing Functions
· Therefore the graph is symmetric about the vertical line \(θ=\dfrac{π}{2}\) This graph has symmetry with respect to the polar axis, the origin, and the vertical line going through the pole To graph the function, tabulate values of \(θ\) between \(0\) and \(π/2\) and then reflect the resulting graphThe usual period is 2 π, but in our case that is "sped up" (made shorter) by the 4 in 4x, so Period = π /2;Sal graphs y=2*sin(x) by considering it as a vertical stretch and a horizontal reflection of y=sin(x) If you're seeing this message, it means we're having trouble loading external resources on our website (π/2) which is 1 so sin(π/2) is going to get you to 1 then sin(π) gets you to 0 sin(3π/2)
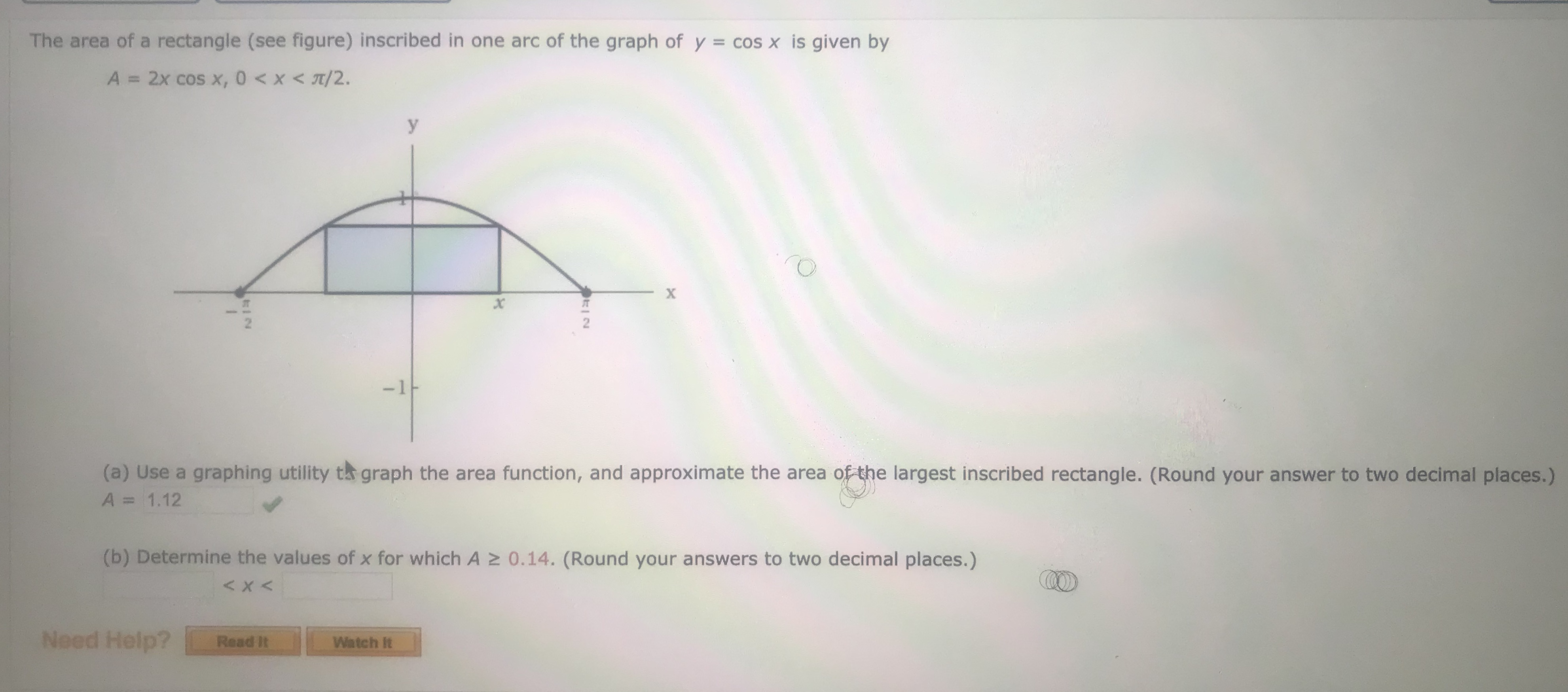


Answered The Area Of A Rectangle See Figure Bartleby
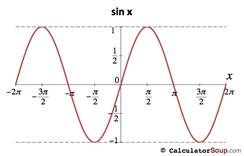


Trigonometric Function Graphs F P
A r Q y x Figure 1 Off center circle r = 2a cos θ √ π 3π, cosθ= − 2 √ 2 in the direction of angle When < θπ, risThe range of arcsin (x) is the domain of f which is given by the interval π/2 , π/2 The graph, domain and range of both f (x) = sin (x) for π/2 ≤ x ≤ π/2 and arcsin (x) are shown below Note that there are 3 key points that may be used to graph arcsin (x) These points are (


Graph Sine And Cosine Functions
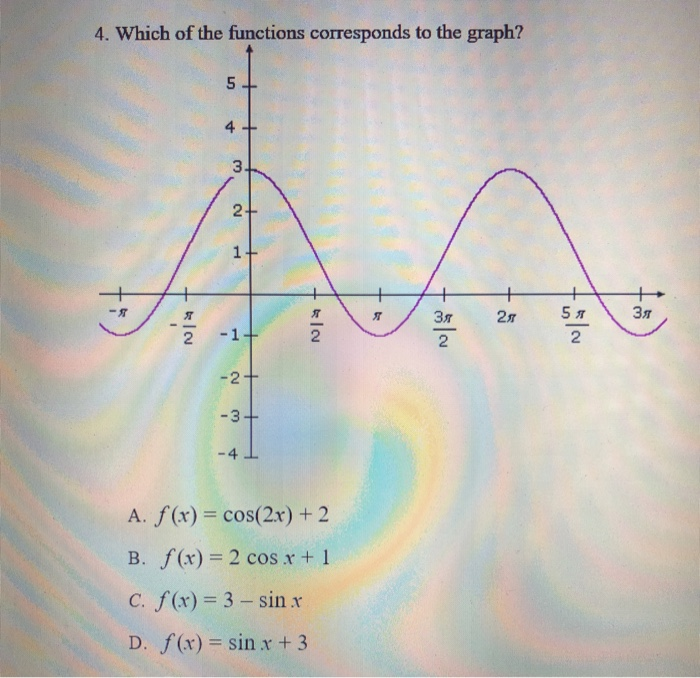


Solved 4 Which Of The Functions Corresponds To The Graph Chegg Com


Solved What Is The Graph Of 2 P


Sine Function And Inverse Sine Function Definition Graph Properties Solved Example Problems



Trigonometric Equations


Discuss Sinusoidal Curves The Graph Of Y Sin X Is The Same As The Graph Of Y Cos X Shifted To The Right P 2 Units So The



Sketch The Following Graphs 1 Y 2 Sin X Pi 4 2 Y 3sin 2x Pi 4 Need The Answer Urgently Sketch Maths Meritnation Com



Graph Of Y Cos 2 X Pi 2 Mathtestpreparation Com
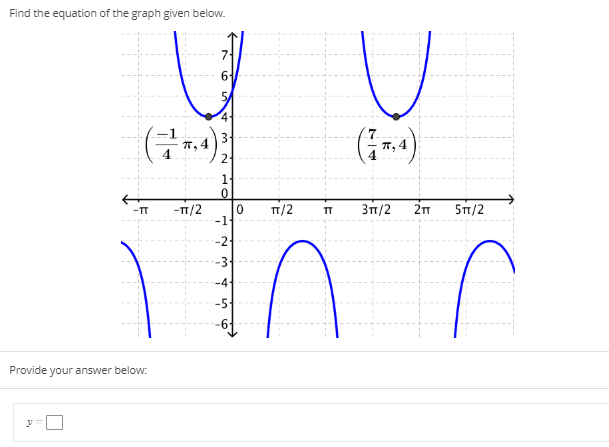


Solved Find The Equation Of The Graph Given Below 6 4 P Chegg Com
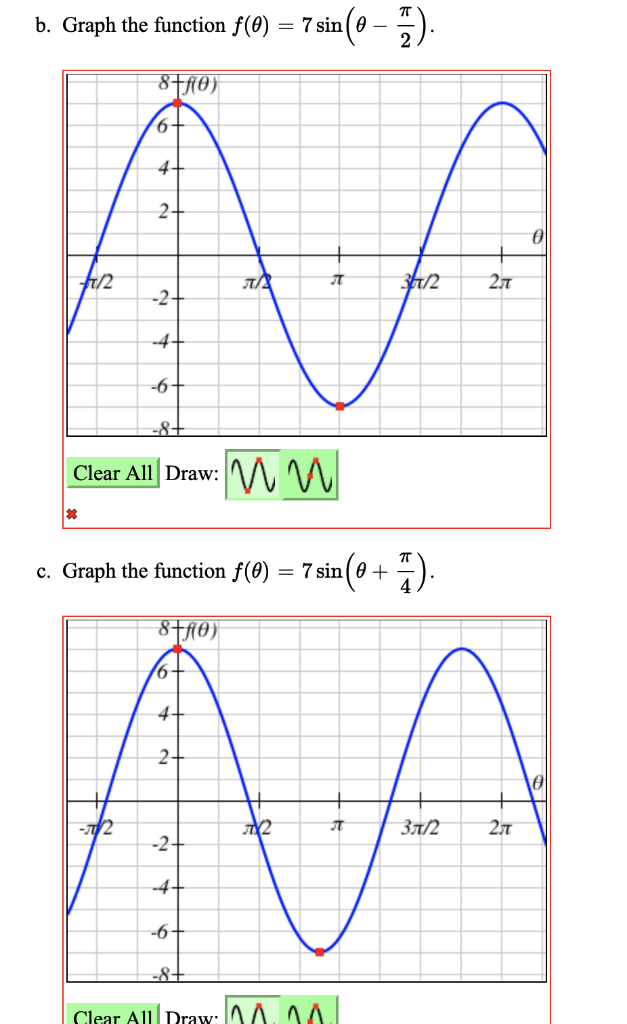


Solved A Graph The Function F 0 7 Sin 8 4 T 2 P 2 6 Chegg Com
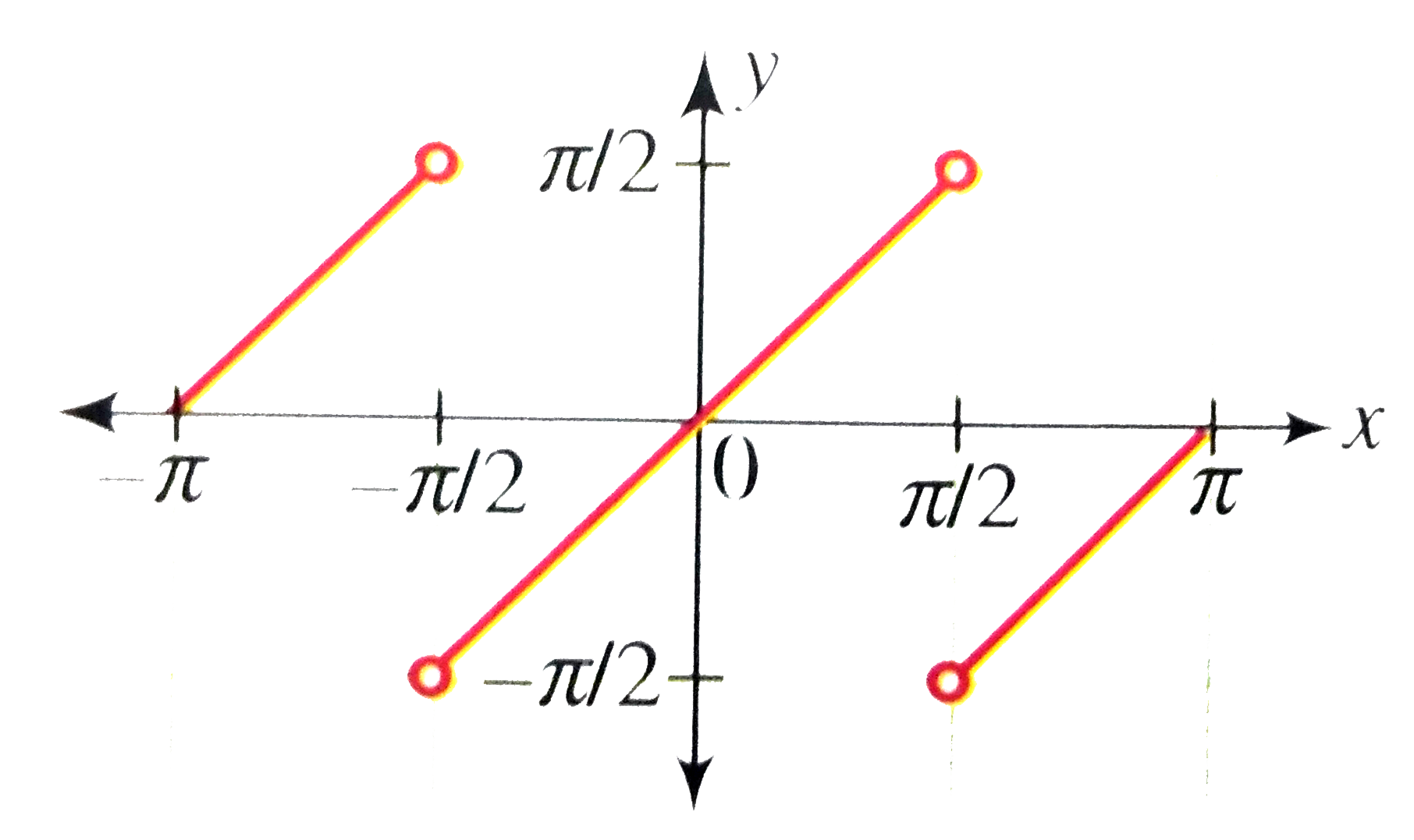


Draw The Graph Of Y Tan 1 2x 1 X 2
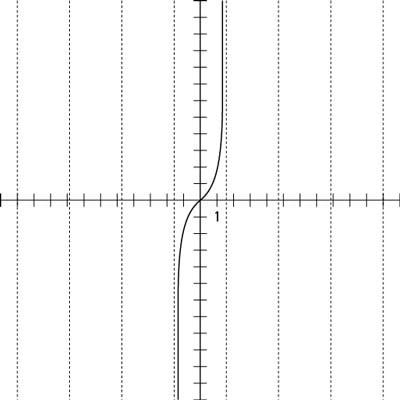


Graph The Asymptote Of A Tangent Function Dummies


Graphing Functions



How Can One Easier Create Nice X Axis Ticks I E Pi 2 Pi 3pi 2 In Ggplot2 Stack Overflow



Polar Coordinates Graphs Algebra And Trigonometry Openstax Cnx


Solution How To Graph Y 2 3 Csc X Pi 2
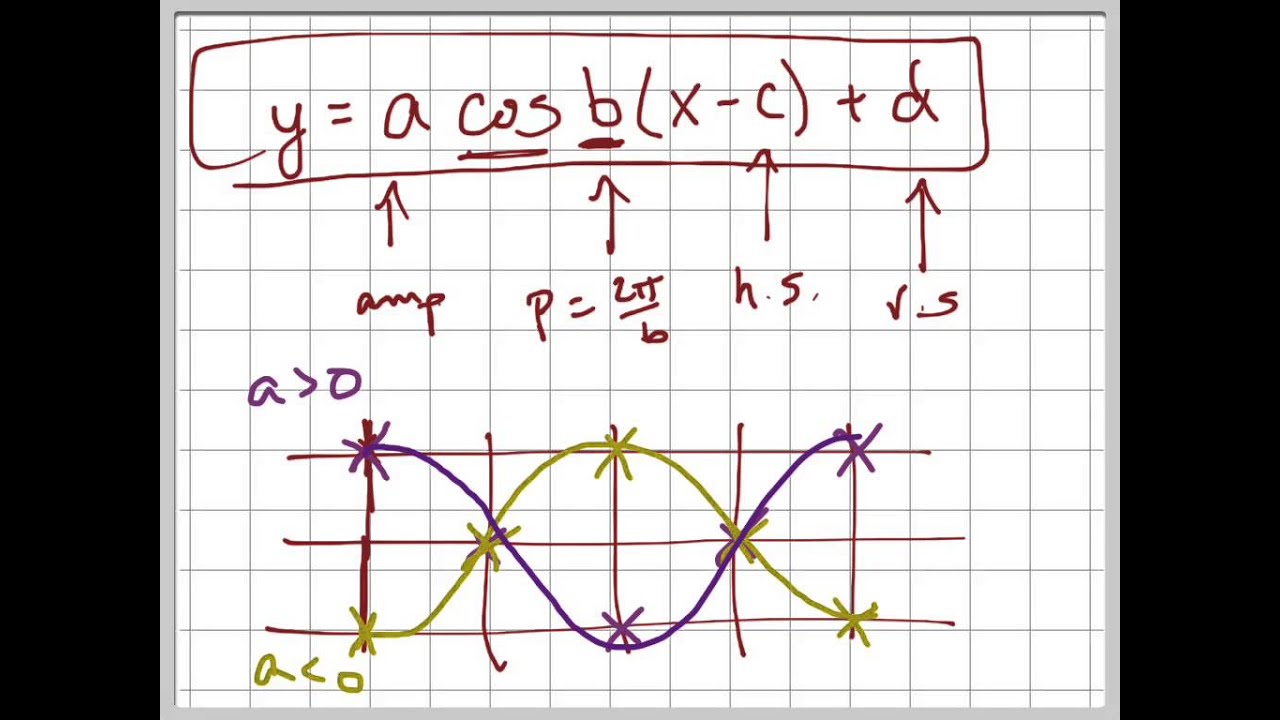


Graph Y 1 3 Cos X P 2 Youtube



Use The Graph And Integral To Find Z Pi 2 Pi 4 2 Pi Pi Study Com
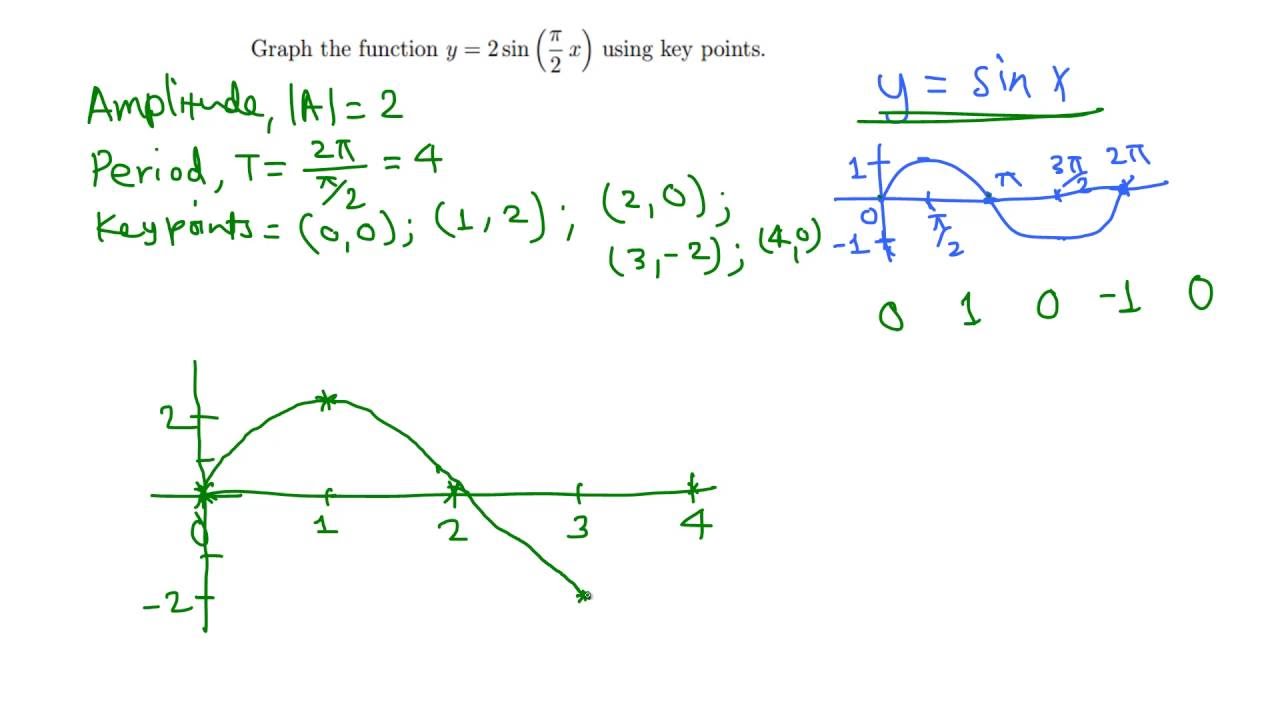


Graph Of Y 2 Sin Pi 2 X Using Key Points Youtube



Graph Of Cosine Function Mathtestpreparation Com


Graphing Tangent Functions



6 5 Translation Of Sine And Cosine Functions


Calculus Revision Maths First Institute Of Fundamental Sciences Massey University


Content Graphing The Trigonometric Functions


Plot Of Cos 2 Pi T
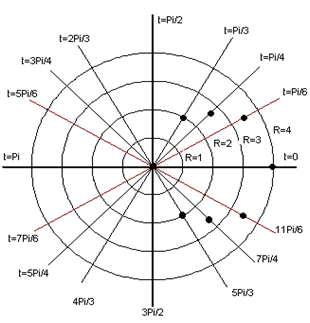


Graphs Of Polar Equations Celestial Tutors
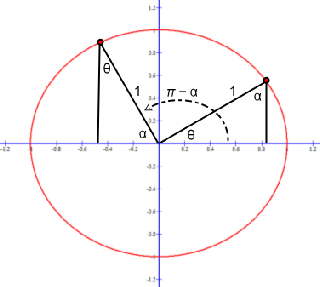


Cosine Graph Trigonometry



Trig Graphs Of The Circular Functions



Graphs Of Sine Function Math Lessons Minneapolis


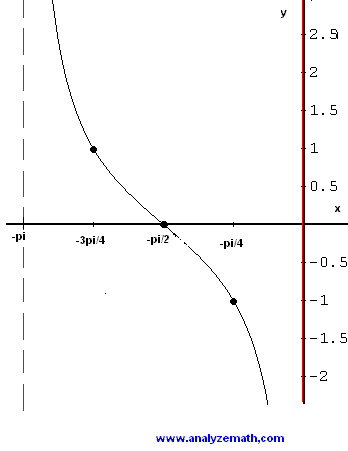
What Is The Graph Of Y Cos X Pi 2 Socratic



Precalculus Polar Coordinates 13 Of 35 Graphing Polar Equations Theta Pi 4 Theta Pi 4 Lines Youtube


Trigonometric Functions And Their Graphs



How To Solve Cos Pi 2 T Ge 0 Mathematics Stack Exchange



Aim What Are The Graphs Of Tangent Function



Find The Value Of Cos Dfrac 5 Pi 2 By Referring To Gauthmath
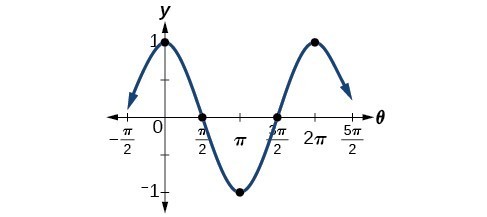


Modeling With Trigonometric Equations Precalculus Ii



Calculus How Is The Answer To Lim X Pi 2 Tan X Negative Infinity And Positive Infinity Quora
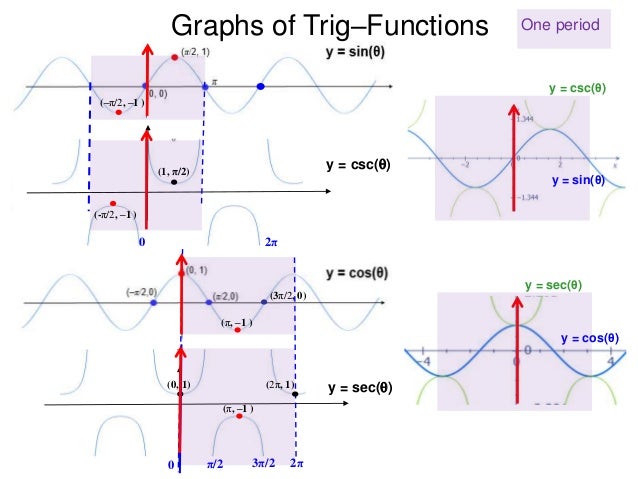


10 Graphs Of Trig Functions X



The Graph Of P 2 X Bottom And 1 Li 2 X Top For 1 X Download Scientific Diagram


Properties Of Graphs Of Trigonometric Functions Opencurriculum



Cosine Function Graph 2 Pi To 2 Pi Radians Graphing Trigonometric Functions Trigonometry



The Inverse Trigonometric Functions Lawsofemotion Definition Of Inverse And One To One Functions An Inverse Function Is A Defined Function That Is Found Using Its Original Function In Order For A
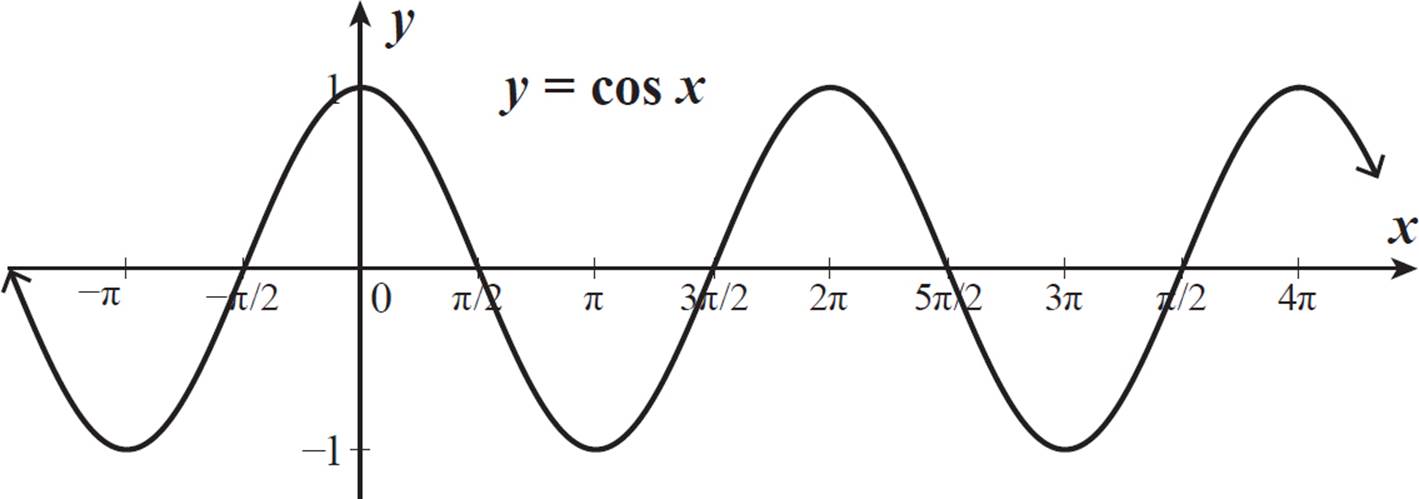


Graphing Trigonometric Functions Trigonometric Functions High School Algebra Ii Unlocked 16


In The Graph The X Axis Is Intersected By The Graph At P 2 3p 2 Act Math Exam Questions With Answers
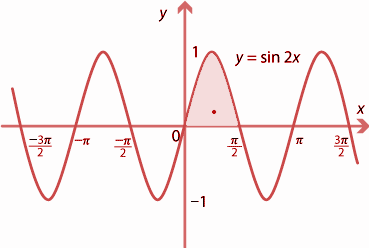


Make A Rough Sketch Of The Graph Y Sin 2x0 Leqslant Class 11 Maths Cbse



Cbse Ncert Notes Class 11 Maths Trigonometric Functions



2 6 Graphs Of The Sine And Cosine Functions Xxy Sin X 00 Sin B2 P 6 Pi 6 Sin P 3 Pi 3 Sin B4 P 2 Pi 2 Sin B5 2p 3 B5 Pi 6 Sin B6 5p 6 B6 Pi 6 Sin Ppt Download
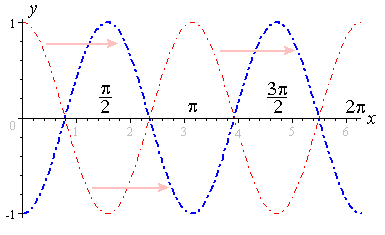


3 Graphs Of Y Asin Bx C And Y Acos Bx C



How Do You Graph Y Sin X Frac Pi 2 Homeworklib



Sketch The Graph For Y Sin 1 Sinx


Which Is The Correct Graph Of Arccot X



Sketch The Graph Of A F T 6 Cos T 3 Pi 2 Leq T Leq 3 Pi 2 B F X Ln 2x 0 X Leq 2 C F X 7e X By Hand And Use Your Sketch


Bay Area Tutoring Blog Archive Graphing Sine And Cosine Functions Like A Pro
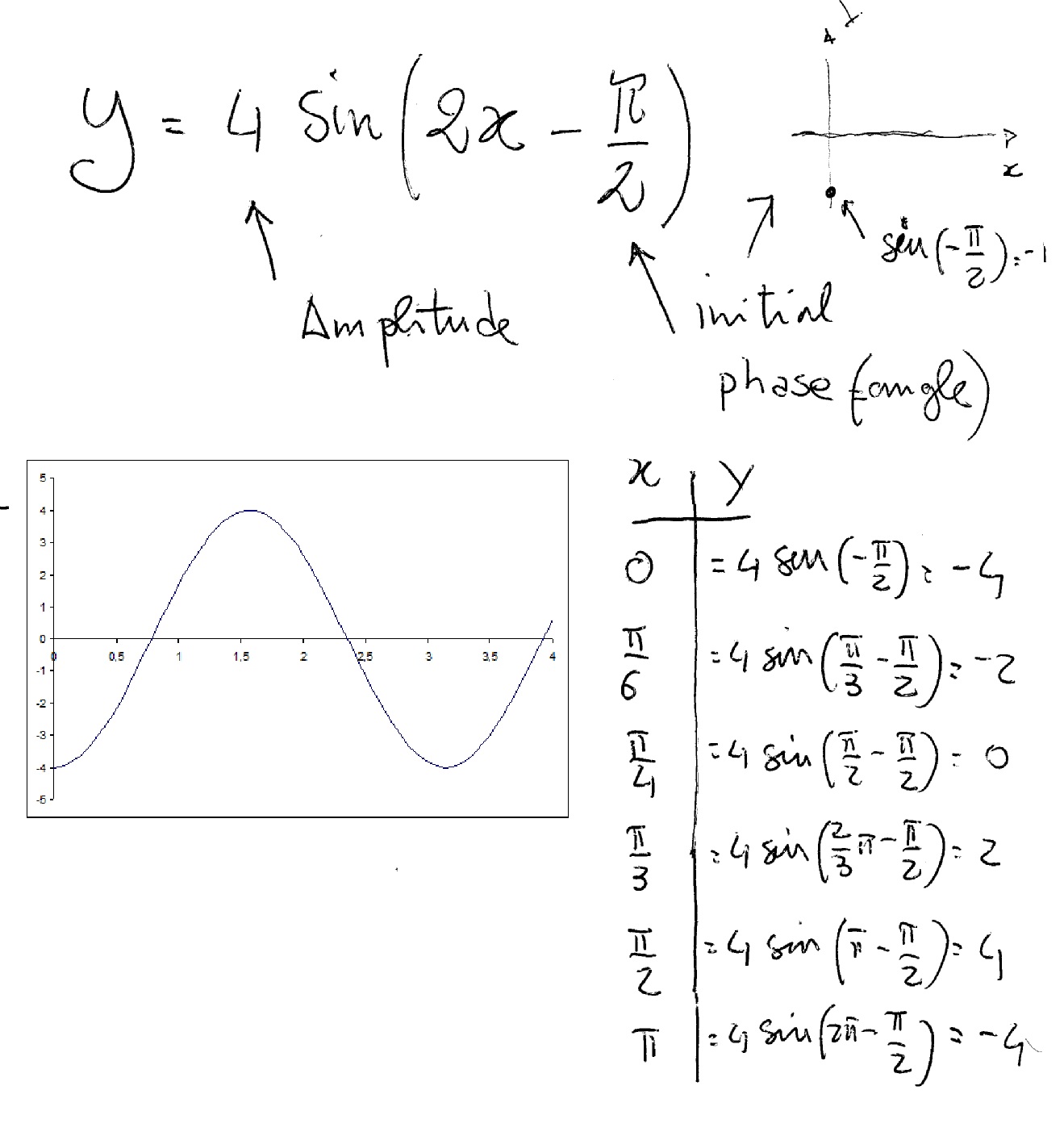


How Do You Graph Y 4sin 2x Pi 2 Socratic
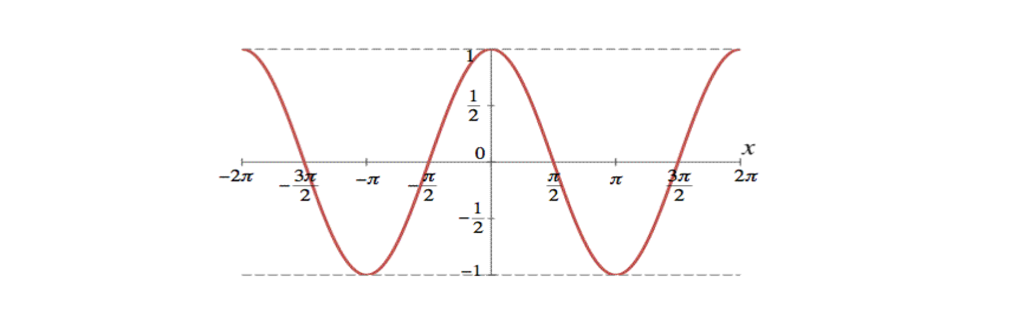


Tangent And Cotangent Graphs Brilliant Math Science Wiki


Modeling With Trigonometric Equations Precalculus


Properties Of Graphs Of Trigonometric Functions Opencurriculum



A Graph Of The Function F X 3 Cos 2x P 2 1 Download Scientific Diagram



Drill For Exam Graph Cie


Ppt Sin Graph Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id


Graphs Of Trigonometric Functions


Assignment 1 Exploring Sine Curves


Graphs Of The Sine And Cosine Function Precalculus Ii


How Do You Find The Value Of Cos Pi 2 Using The Graph Socratic



The Graph Of The Function E On The Interval P 2 P Download Scientific Diagram


If Sin X 1 2 And X Is Between Pi 2 And 3pi 2 What Is The Value Of X 2 The Answer Key Says It Is 5pi 12 But I Have No Clue How To
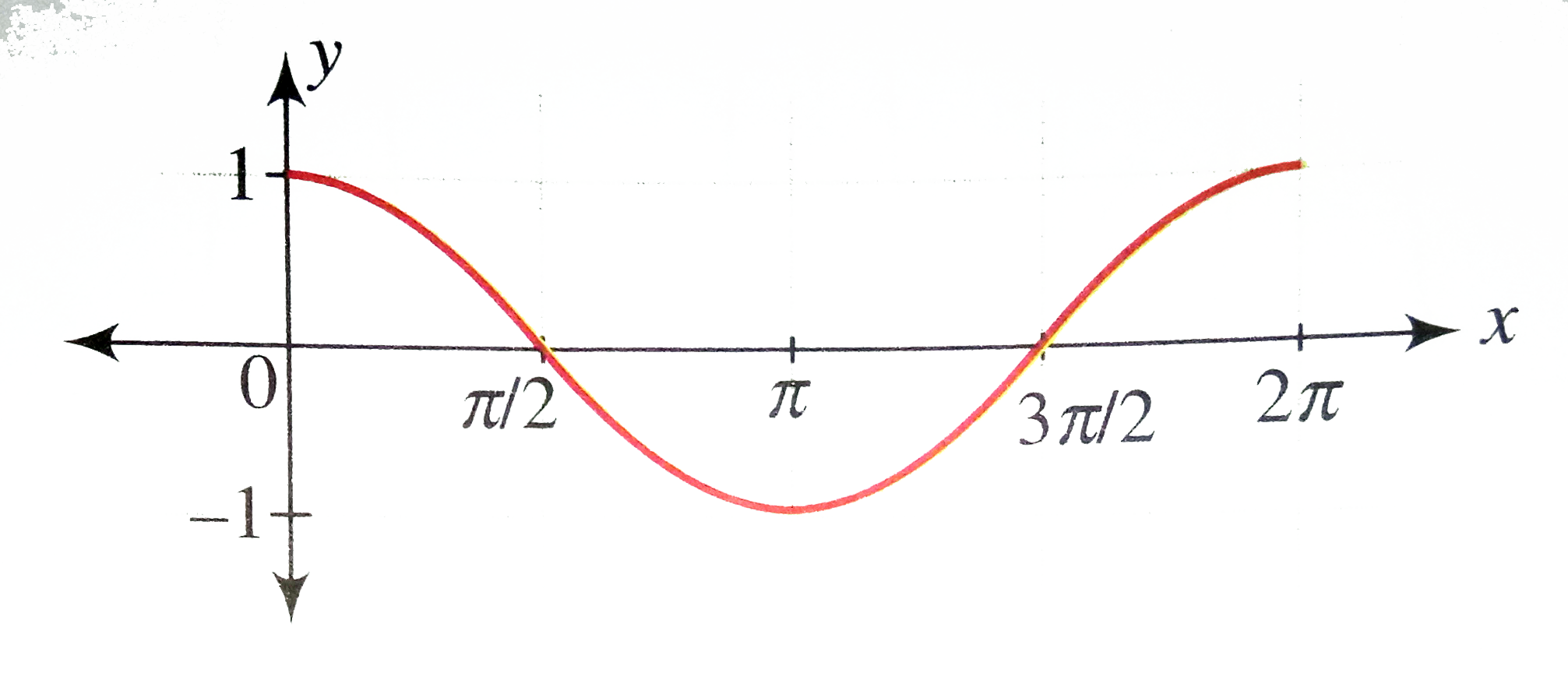


Draw The Graph Of Y Cos X X In 0 2pi Where Represents
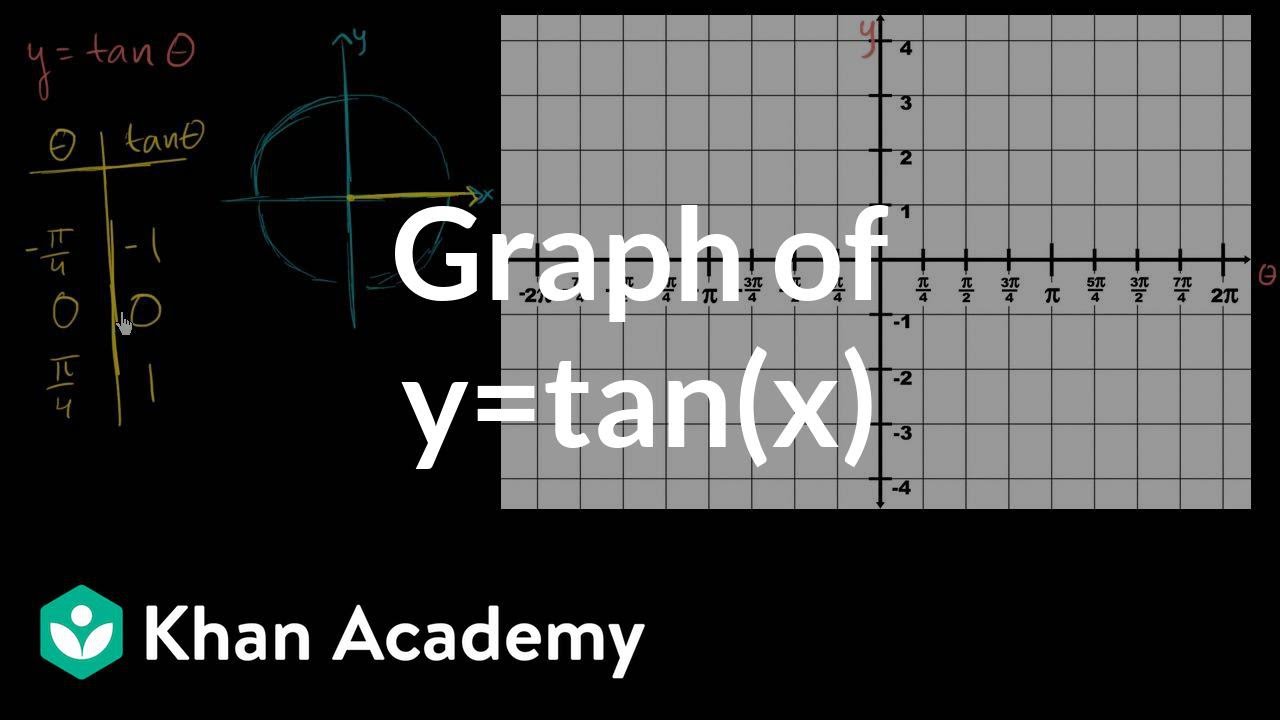


Graph Of Y Tan X Video Trigonometry Khan Academy



Choose The Correct Equation S For The Function Shown In The Graph Select All That Apply There Is Brainly Com


From The Curve Y Sin X Graph The Functions I Y Sin X Ii Y Sin X Iii Y Sin P 2 X Which Is Cos X Sarthaks Econnect
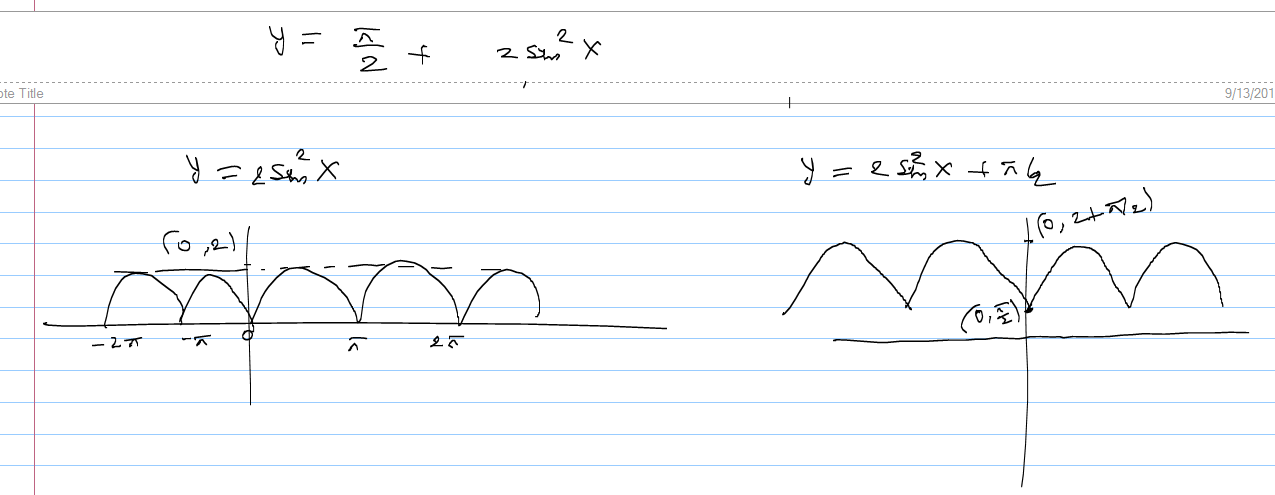


Draw The Graph Of Y P 2 2sin 2x Please Help Fast Askiitians



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿